Have you ever thought what are libraries in Android and how to build them?

When I started as an Android dev about 1.5 years back, I used to think, why do I need libraries when I can build all that cool stuff myself? However, as I completed about 2 months in the profession I started realizing the importance of the library and re-inventing the wheel every time was not at all a good idea. Every time I used a library from GitHub, I used to think, how do they build such cool library and how is it different from the normal app which I was used to building? If you wonder the same, you are in the right place. Today I will be explaining what libraries are, how you can build them, also why and how to distribute a library you built.
What is a library?
To know what is a library, you must know what a module is. Let’s learn what a module is.
A Module in a project follows the Separation of Concern (S) from the SOLID principles of Object-Oriented Design.[*] Modules help in splitting a project into smaller modules which would run independently or dependently on other modules.
Whenever we create a new project, Android Studio creates a single module which is an application module or app in short. App modules can run independently. Whereas, library modules cannot run independently. It is dependent on another application module which will invoke this library module for it to run. In Android, all of this is handled via build.gradle file of the application module.
Why should I build them?
When we work on multiple projects, we often write a lot of components in our project which we later need in other projects as well. What we end up doing is copy-pasting the code from project one to project two. Later we find that there was a bug in the component and we fix them in project two. However, the bug still exists in project one. Maintaining the same codebase twice is a challenging task and is not the best way to do it.
The best way to handle such a situation is to convert the component to separate library modules. This module can then be imported into both the projects. This also makes maintenance of this component easier and no copy paste needed, Yay!!. Here we are sharing the module (library) locally. But can’t this be done globally? Where one person writes components and makes it available for any developer to use it. If any developer using this component finds a bug, he can report it to the creator and wait for him to fix it or fix it himself. We all developers live in peace. 🙂
How to build a library?
-
Let’s create a new empty project in Android and name it “MyApp”. On completing of creating a new project, the “Project” pane of Android Studio will look like this.
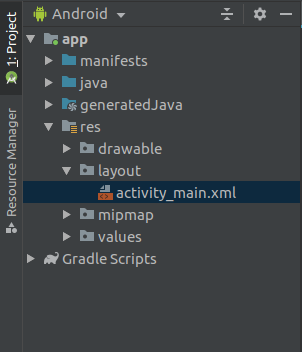 Congratulations we have successfully created a new module. However, this is not the type of module we are here for. This is an application module, what we need is a library module. So let’s create one
Congratulations we have successfully created a new module. However, this is not the type of module we are here for. This is an application module, what we need is a library module. So let’s create one -
Go to
File -> New -> New module…it will show us a popup asking for the type of module you want to add. Select “Android Library” from the list and click Next and then it will ask us to name our module. Let’s name it “My Library” and click Finish. After we complete this step our project pane will look like this.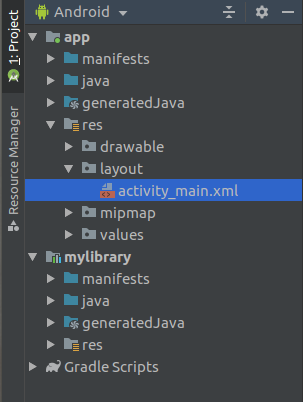 Notice the
Notice the mylibrarythere? That’s the new library module which we just created. Android studio differentiate between them by showing a different icon for the app module and library module.
How does Android Studio know which one is an app module and which one is a library module? What changed? The answer is hidden inside the module level build.gradle file. If you open the app and library modules’ build.gradle you will see the first line of app’s Gradle file is
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
and that of the library is
apply plugin: 'com.android.library'
This is what tells Android Studio what type of Module it is. Now we can write all of our fancy code inside the library module which we want to distribute.
Pro Tip: It’s considered good practice to make your library code configurable for most common use cases. Because, what we build our library for might not be the exact use case for the developer using the library.
How do I use this library module in my app?
Simple!! you just have to add one lie to your app module-level build.gradle file
implementation project(path: ':mylibrary')
This will only work if your module is in the same project as your app.
If your library module is in some other project, you will have to import it to your current project or publish that library through JCenter. About which I will explain in my next post.
Since you have added this library as a dependency to the app module, now you can use the code/feature from the library as if it is a part of your project.
